Buttons & LED
There are 3 essential parts in a complete automatic control device:
- INPUT: Buttons, switches, sensors, etc.
- OUTPUT: LED, buzzer, motor.
- CONTROL: RPi, Arduino, microcontroller.
This example explains how to build a simple control system of an LED using a push button switch.
Circuit
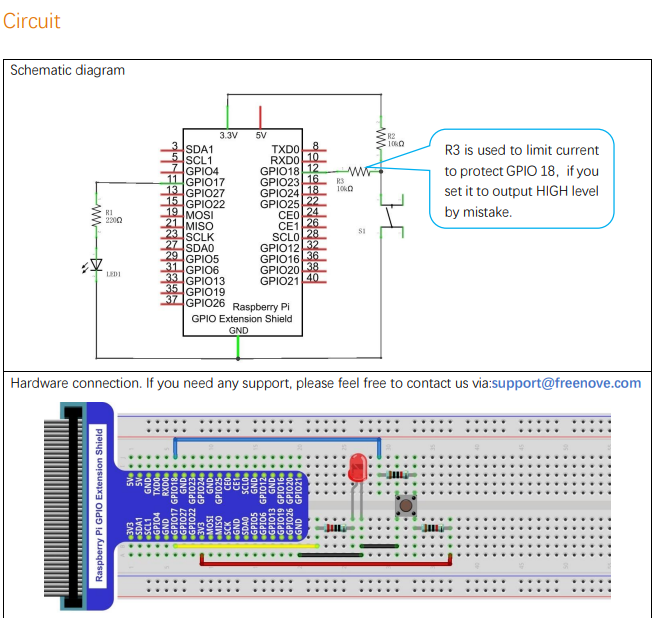
Code
C
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ledPin 0 //define the ledPin
#define buttonPin 1 //define the buttonPin
void main(void)
{
printf("Program is starting ... \n");
wiringPiSetup(); //Initialize wiringPi.
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); //Set ledPin to output
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);//Set buttonPin to input
pullUpDnControl(buttonPin, PUD_UP); //pull up to HIGH level
while(1){
if(digitalRead(buttonPin) == LOW){ //button is pressed
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); //Make GPIO output HIGH level
printf("Button is pressed, led turned on >>>\n"); //Output information on terminal
}
else { //button is released
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); //Make GPIO output LOW level
printf("Button is released, led turned off <<<\n"); //Output information on terminal
}
}
}
gcc ButtonLED.c -o ButtonLed -lwiringPi
Python
ButtonLED.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
ledPin = 11 # define ledPin
buttonPin = 12 # define buttonPin
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # use PHYSICAL GPIO Numbering
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # set ledPin to OUTPUT mode
GPIO.setup(buttonPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # set buttonPin to PULL UP INPUT mode
def loop():
while True:
if GPIO.input(buttonPin)==GPIO.LOW: # if button is pressed
GPIO.output(ledPin,GPIO.HIGH) # turn on led
print ('led turned on >>>') # print information on terminal
else : # if button is relessed
GPIO.output(ledPin,GPIO.LOW) # turn off led
print ('led turned off <<<')
def destroy():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW) # turn off led
GPIO.cleanup() # Release GPIO resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program entrance
print ('Program is starting...')
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Press ctrl-c to end the program.
destroy()